The Scene
Capital One’s pitch for its Discover deal does little to address what are likely to be regulators’ biggest concerns, critics say, and tees up what’s expected to be a contentious battle against government officials already spoiling for a fight.
In its lengthy application to regulators, Capital One says the $35 billion takeover won’t hurt competition because the combined company will only account for 14% of purchases made by credit cards, the company’s preferred metric.
That shows it’s living in the “regulatory past,” says Jeremy Kress, a University of Michigan professor who focuses on bank regulation.
“It’s like [Capital One’s lawyers at] Wachtell took the template from the last 20 deals and did a control+ F,” Kress said in an interview. “Times have changed, and the people making the decisions on this merger are not the same regulators as before.”
Kress said Capital One’s analysis ignores submarkets and niches that regulators are likely to focus on. Subprime is “a totally different animal than cards with $800 annual fees and access to airport lounges,” he said.
Capital One and Discover are among the biggest issuers of credit cards to people with poor credit scores, generally under 660. Doing some rough math, Kress calculates that combining them would exceed the Justice Department’s own limits on market concentration. They are also both big issuers of secured credit cards, which require a deposit and are used to help people build or rebuild credit after a bankruptcy.
If banking regulators approve the deal, the DOJ could still file its own suit, and its antitrust chief has shown a special interest in bank mergers. Jonathan Kanter said in a speech last June that the department should update its rules for bank consolidation, which were last revised in 1995. “A lot has changed since then, but curiously our bank merger guidelines have not,” he said.
Despite the competition crackdown in Washington, Capital One initially declined to hire outside advisers to steer them through the hostile regulatory environment, people familiar with the matter said. They have since done so as the heat from Washington has ratcheted up.
In this article:
Liz’s view
Capital One’s best argument would seem to be that the merger would bust up the Visa-Mastercard duopoly. It’s certainly a satisfying one: Visa and Mastercard facilitate three-quarters of U.S. credit-card transactions and are consistently among the most profitable companies in the S&P 500. American Express has 20% of the market and Discover has about 4%, and both have lost ground over the past decade. Capital One is right when it says they “sorely need an injection of competitive rivalry.”
But this deal won’t really do that. Understanding why requires a dive into the payment processing ecosystem.
Visa and Mastercard compete by offering banks that issue credit cards, like JPMorgan and PNC, a bigger slice of swipe fees in exchange for choosing their network. Discover doesn’t. It operates a closed loop, where its network supports only its own credit cards, and Capital One’s pitch to regulators doesn’t include any plans to change that.
Instead, Capital One will eventually run its own 100 million cards, which today are split between Visa and Mastercard, over Discover’s rails. That would boost Discover’s share to as much as 15% of the market, so Capital One is right that the deal would “deconcentrate these … markets over which Visa and Mastercard tower.” But that’s not the same thing as increased competition, and unless there’s a chance that in the future, your Chase card will have a Discover logo instead of a Visa one, this deal will do little to shake things up.
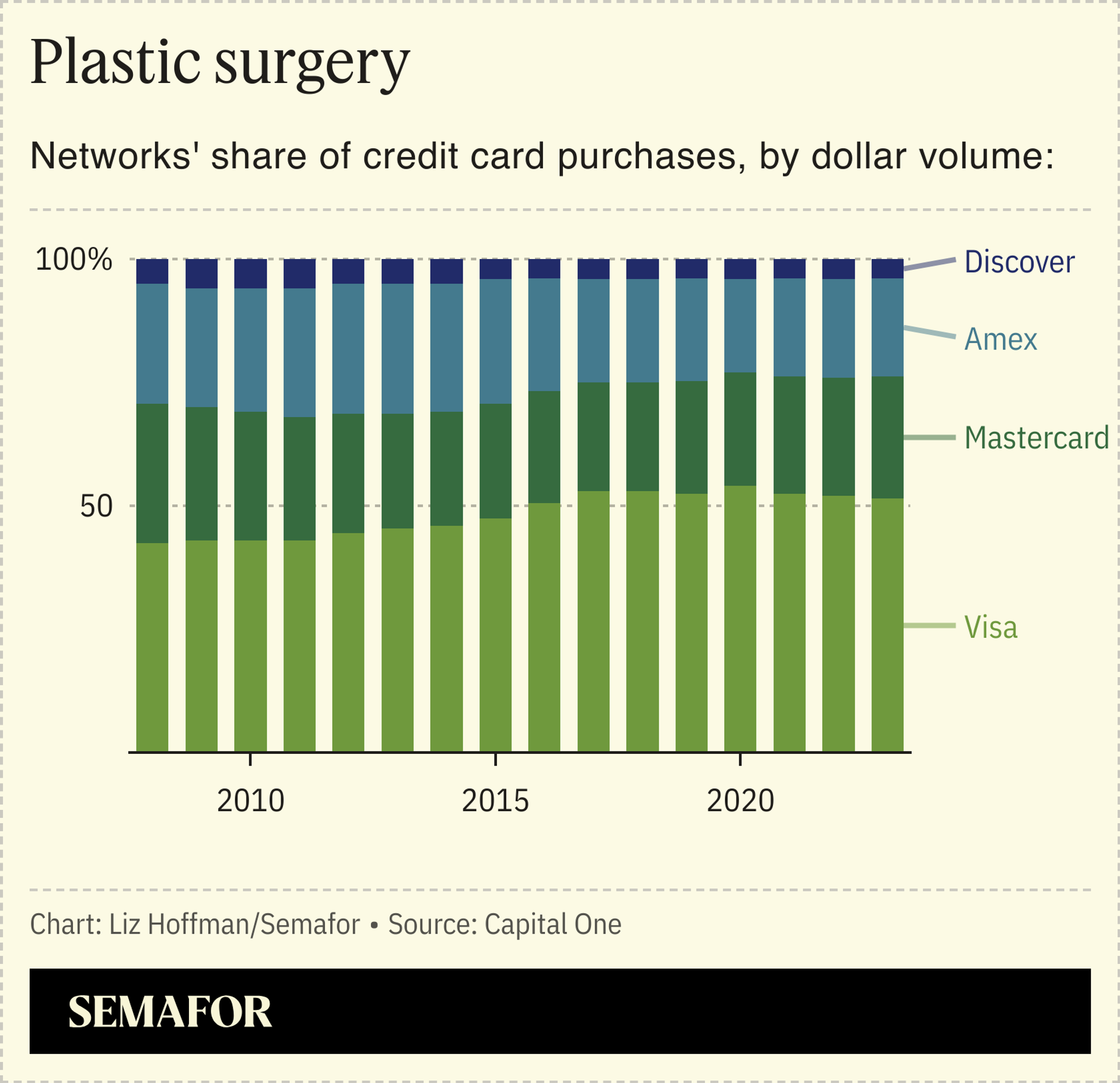
If anything, Capital One is building a competitor to American Express, which, like Discover, issues its own credit cards and runs them on its own network. But Amex and Discover don’t compete for customers. Amex offers elite perks to rich people, while one-fifth of Discover’s cardholders have credit scores under 660, and Amex’s average transaction size is three times bigger.
Another of the company’s pro-competition arguments — that the merged company’s size will force more merchants to accept Discover cards — falls flat. Discover is already accepted at 99% of merchants that take credit cards. This argument is also dangerous: If a combined Capital One-Discover is big enough to force stores to accept its cards, it’s big enough to foist higher fees on them, too. (Amex charges more than Visa and Mastercard.) Capital One is right that most merchants can’t afford to blacklist the country’s largest credit card issuer, but that cuts two ways.
Its best argument may be what it can do for merchants, which have long hated Visa and Mastercard’s stranglehold. Capital One has a nascent shopping app, which partners with retailers to offer special deals to customers. Its 170 million cardholders post-merger, and Discover’s ties to merchants through its network, make that a more efficient process. And a landmark legal settlement last week, which gives merchants more discretion to offer discounts on certain cards, makes it a more attractive prospect for retailers.
Capital One disputes that subprime cards are a defined market, noting that customers move in and out of them as their credit scores change and that nothing is stopping banks from getting in the game.
But antitrust regulators can define markets however they want. Office Depot and Staples called off their 2016 merger after they tried, and failed, to convince a federal judge to consider the rise of Amazon, and not just competition between brick-and-mortar stores. Sysco and U.S. Foods had their merger blocked in 2015 after regulators chose to view food-wholesaling competition nationally, rather than locally.
Capital One will try to get regulators to take a broad view of credit and sweep in alternative products like “buy now, pay later” microloans, which have grown into a $300 billion market that the Kansas City Fed has said might replace credit cards. It will argue that cards aimed at borrowers with lower credit scores and less income are too squishy and fluid a market to examine.
It might work. Or they might get Staples-ed.
Room for Disagreement
Wharton professor Herbert Hovenkamp doubts that regulators will look too closely at subprime credit cards, or be bothered by Capital One and Discover’s combined heft there.

Notable
- “Owning networks in both credit and debit payment ecosystems also allows Capital One to go from being a toll-payer on the payment network highway to a toll-collector,” writes the the American Economic Liberties Project, a think tank run by Matt Stoler, dubbed “America’s angriest progessive” by Politico.
